CCNA 4 R&S: Connecting Networks Chapter 4 v5.02 + v5.03 Exam Answers 2016
1.
What is a characteristic of Frame Relay that provides more flexibility than a dedicated line?
What is a characteristic of Frame Relay that provides more flexibility than a dedicated line?
Customers use dedicated circuits in increments of 64 kb/s.
Dedicated physical circuits are installed between each site.
The Frame Relay cloud allocates as much bandwidth as required to active PVCs to maintain the connection.
One router WAN port can be used to connect to multiple destinations.
Dedicated physical circuits are installed between each site.
The Frame Relay cloud allocates as much bandwidth as required to active PVCs to maintain the connection.
One router WAN port can be used to connect to multiple destinations.
2
What are the two major criteria that constitute the cost of a Frame Relay circuit? (Choose two.)
What are the two major criteria that constitute the cost of a Frame Relay circuit? (Choose two.)
QoS
end-to-end connectivity
local loop
required bandwidth
circuit management fees
end-to-end connectivity
local loop
required bandwidth
circuit management fees
3
A router interface connects to a Frame Relay network over a preconfigured logical circuit that does not have a direct electrical connection from end to end. Which type of circuit is being used?
A router interface connects to a Frame Relay network over a preconfigured logical circuit that does not have a direct electrical connection from end to end. Which type of circuit is being used?
SVC
hub and spoke
full mesh
dedicated leased line
PVC
hub and spoke
full mesh
dedicated leased line
PVC
4
Which Frame Relay topology provides a connection from every site to every other site and maintains a high amount of reliability?
Which Frame Relay topology provides a connection from every site to every other site and maintains a high amount of reliability?
hub and spoke
partial mesh
full mesh
star
partial mesh
full mesh
star
5
Which technology allows a Layer 3 IPv4 address to be dynamically obtained from a Layer 2 DLCI?
Which technology allows a Layer 3 IPv4 address to be dynamically obtained from a Layer 2 DLCI?
Neighbor Discovery
Address Resolution Protocol
Inverse Neighbor Discovery
Inverse Address Resolution Protocol
Address Resolution Protocol
Inverse Neighbor Discovery
Inverse Address Resolution Protocol
6
A network administrator has statically configured the LMI type on the interface of a Cisco router that is running Cisco IOS Release 11.2. If the service provider modifies its own LMI type in the future, what step must the network administrator take?
A network administrator has statically configured the LMI type on the interface of a Cisco router that is running Cisco IOS Release 11.2. If the service provider modifies its own LMI type in the future, what step must the network administrator take?
The network administrator must modify the keepalive time interval to maintain connectivity with the LMI type of the service provider.
The network administrator does not have to do anything, because all LMI types are compatible with one another.
The network administrator must statically set the LMI type to be compatible with the service provider.
The network administrator simply has to verify connectivity with the provider, because the router has an LMI autosensing feature that automatically detects the LMI type.
The network administrator does not have to do anything, because all LMI types are compatible with one another.
The network administrator must statically set the LMI type to be compatible with the service provider.
The network administrator simply has to verify connectivity with the provider, because the router has an LMI autosensing feature that automatically detects the LMI type.
7
Which two functions are provided by the Local Management Interface (LMI) that is used in Frame Relay networks? (Choose two.)
Which two functions are provided by the Local Management Interface (LMI) that is used in Frame Relay networks? (Choose two.)
mapping of DLCIs to network addresses
error notification
congestion notification
simple flow control
exchange of information about the status of virtual circuits
error notification
congestion notification
simple flow control
exchange of information about the status of virtual circuits
8
Which parameter would be specified in a Frame Relay provider contract for a particular company?
Which parameter would be specified in a Frame Relay provider contract for a particular company?
DE
QoS
Inverse ARP enabled/disabled
CIR
QoS
Inverse ARP enabled/disabled
CIR
9
Which three notification mechanisms are used when congestion is present in a Frame Relay network? (Choose three.)
Which three notification mechanisms are used when congestion is present in a Frame Relay network? (Choose three.)
DE
BECN
inverse ARP
CIR
FECN
DLCI
BECN
inverse ARP
CIR
FECN
DLCI
10
Why would a customer request a Frame Relay circuit with a CIR of zero?
Why would a customer request a Frame Relay circuit with a CIR of zero?
to have a circuit used for network management traffic
to have a backup circuit for critical data transmissions
to have better QoS
to have a link with reduced costs
to have a circuit used for voice traffic
to have a backup circuit for critical data transmissions
to have better QoS
to have a link with reduced costs
to have a circuit used for voice traffic
11
Which provider-negotiated parameter would allow a customer to send data above the rate of the bandwidth specified by the CIR?
Which provider-negotiated parameter would allow a customer to send data above the rate of the bandwidth specified by the CIR?
DE
FECN
Be
Bc
FECN
Be
Bc
12
What is the purpose of applying the command frame-relay map ip 10.10.1.2 110 broadcast?
What is the purpose of applying the command frame-relay map ip 10.10.1.2 110 broadcast?
to support IPv6 traffic over the NBMA network by using DLCI 110
to allow Frame Relay frames to be broadcast over DLCI 110
to allow Frame Relay frames to be broadcast toward host 10.10.1.2
to allow Frame Relay frames to be broadcast on all Frame Relay interfaces
to configure a device with a static Frame Relay map that also allows the forwarding of routing updates
to allow Frame Relay frames to be broadcast over DLCI 110
to allow Frame Relay frames to be broadcast toward host 10.10.1.2
to allow Frame Relay frames to be broadcast on all Frame Relay interfaces
to configure a device with a static Frame Relay map that also allows the forwarding of routing updates
13
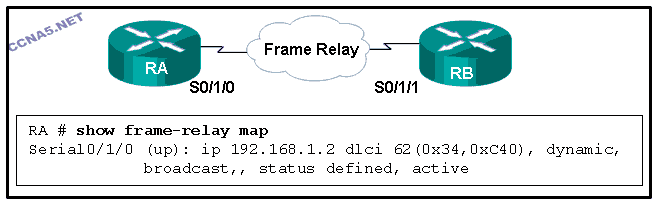
Refer to the exhibit. Which two statements are correct? (Choose two.)
The IPv4 address of interface S0/1/0 on RA is 192.168.1.2.
The IPv4 address of interface S0/1/1 on RB is 192.168.1.2.
The DLCI that is attached to the VC on RA to RB is 62.
The DLCI that is attached to the VC on RB to RA is 62.
The Frame Relay map was set by using the command frame-relay map.
The IPv4 address of interface S0/1/1 on RB is 192.168.1.2.
The DLCI that is attached to the VC on RA to RB is 62.
The DLCI that is attached to the VC on RB to RA is 62.
The Frame Relay map was set by using the command frame-relay map.
14

Refer to the exhibit. Which statement is true about Frame Relay traffic on R1?
Traffic that exits subinterface Serial 0/0/0.102 is marked with DLCI 201.
Traffic on Serial 0/0/0 is experiencing congestion between R1 and the Frame Switch.
Traffic that is mapped to DLCI 201 will exit subinterface Serial 0/0/0.201.
Frames that enter router R1 from a Frame Relay neighbor will have DLCI 201 in the frame header.
Traffic on Serial 0/0/0 is experiencing congestion between R1 and the Frame Switch.
Traffic that is mapped to DLCI 201 will exit subinterface Serial 0/0/0.201.
Frames that enter router R1 from a Frame Relay neighbor will have DLCI 201 in the frame header.
15
Which three actions can be taken to solve Layer 3 routing protocol router reachability issues when using Frame Relay? (Choose three.)
Which three actions can be taken to solve Layer 3 routing protocol router reachability issues when using Frame Relay? (Choose three.)
Use subinterfaces.
Disable Inverse ARP.
Use a full mesh topology.
Use the keyword cisco as the LMI type.
Disable split horizon.
Configure static DLCI mappings.
Disable Inverse ARP.
Use a full mesh topology.
Use the keyword cisco as the LMI type.
Disable split horizon.
Configure static DLCI mappings.
16
When would the multipoint keyword be used in Frame Relay PVCs configuration?
When would the multipoint keyword be used in Frame Relay PVCs configuration?
when multicasts must be supported
when using physical interfaces
when participating routers are in the same subnet
when global DLCIs are in use
when using physical interfaces
when participating routers are in the same subnet
when global DLCIs are in use
17
A network engineer has issued the interface serial 0/0/1.102 point-to-point command on a router that will be communicating with another router over a Frame Relay virtual circuit that is identified by the DLCI 102. Which two commands would be appropriate for the network engineer to issue next? (Choose two.)
A network engineer has issued the interface serial 0/0/1.102 point-to-point command on a router that will be communicating with another router over a Frame Relay virtual circuit that is identified by the DLCI 102. Which two commands would be appropriate for the network engineer to issue next? (Choose two.)
no shutdown
no ip address
encapsulation frame relay
ip address 10.1.1.10 255.255.255.252
frame-relay interface-dlci 102
no ip address
encapsulation frame relay
ip address 10.1.1.10 255.255.255.252
frame-relay interface-dlci 102
18
Which two Frame Relay router reachability issues are resolved by configuring logical subinterfaces? (Choose two.)
Which two Frame Relay router reachability issues are resolved by configuring logical subinterfaces? (Choose two.)
LMI status inquiry messages sent to the network are not received.
Inverse ARP fails to associate all IP addresses to the correct DLCIs.
Frame Relay is unable to map a remote IP address to a DLCI.
Distance vector routing protocols are unable to forward routing updates back out the incoming interface to other remote routers.
Link-state routing protocols are unable to complete neighbor discovery.
Inverse ARP fails to associate all IP addresses to the correct DLCIs.
Frame Relay is unable to map a remote IP address to a DLCI.
Distance vector routing protocols are unable to forward routing updates back out the incoming interface to other remote routers.
Link-state routing protocols are unable to complete neighbor discovery.
19
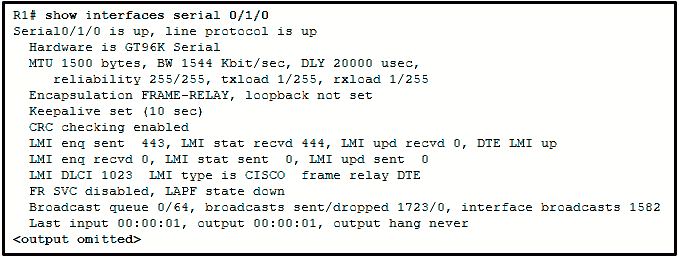
Refer to the exhibit. A network administrator has implemented the show interfaces serial 0/1/0 command. What can be verified from the displayed output?
Router R1 connects to multiple sites through the serial 0/1/0 interface.
Router R1 is forwarding traffic on interface serial 0/1/0 using the local DLCI 1023.
Router R1 is not using the default LMI type.
Router R1 has been configured with Frame Relay via the ietf keyword.
Router R1 is forwarding traffic on interface serial 0/1/0 using the local DLCI 1023.
Router R1 is not using the default LMI type.
Router R1 has been configured with Frame Relay via the ietf keyword.
20
The show frame-relay pvc command is best utilized to display the number for which type of packets that are received by the router?
The show frame-relay pvc command is best utilized to display the number for which type of packets that are received by the router?
FECN and BECN messages
Inverse Neighbor Discovery messages
Inverse ARP messages
LMI status messages
Inverse Neighbor Discovery messages
Inverse ARP messages
LMI status messages
21
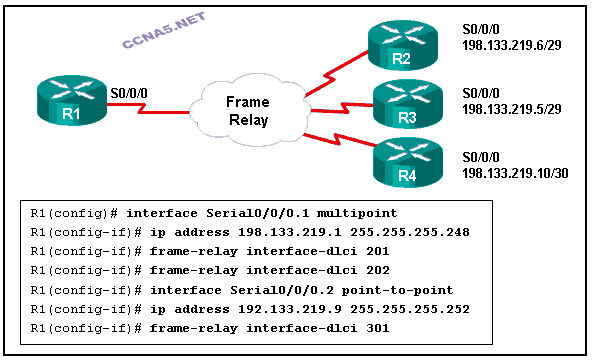
Refer to the exhibit. A network administrator is configuring Frame Relay subinterfaces on R1. A distance vector routing protocol has also been configured. Data is routing successfully from R1 to networks that are connected to R2, R3, and R4, but routing updates between R2 and R3 are failing. What is the possible cause of this failure?
Split horizon is preventing successful routing table updates on the multipoint link.
Multipoint Frame Relay networks cannot be used with this IP addressing scheme.
Subinterfaces cannot be used on multipoint Frame Relay links.
Two DLCI identifiers cannot be configured on one subinterface.
Multipoint Frame Relay networks cannot be used with this IP addressing scheme.
Subinterfaces cannot be used on multipoint Frame Relay links.
Two DLCI identifiers cannot be configured on one subinterface.
22

Refer to the exhibit. A network administrator issues the show frame-relay map command to troubleshoot the Frame Relay connection problem. Based on the output, what is the possible cause of the problem?
The S0/0/1 interface of the R2 router is down.
The IP address on S0/0/1 of R3 is configured incorrectly.
Inverse ARP is providing false information to the R1 router.
The S0/0/1 interface of the R2 router has been configured with the encapsulation frame relay ietfcommand.
The Frame Relay map statement on the R3 router for the PVC to R2 is configured with an incorrect DLCI number.
The IP address on S0/0/1 of R3 is configured incorrectly.
Inverse ARP is providing false information to the R1 router.
The S0/0/1 interface of the R2 router has been configured with the encapsulation frame relay ietfcommand.
The Frame Relay map statement on the R3 router for the PVC to R2 is configured with an incorrect DLCI number.
23
Fill in the blank. Use an acronym.
The Frame Relay “DLCI” identifies a connection from one endpoint to a remote destination.
Fill in the blank. Use an acronym.
The Frame Relay “DLCI” identifies a connection from one endpoint to a remote destination.
24
Fill in the blank.
The encapsulation frame-relay “ietf” command enables Frame Relay encapsulation and allows connection to a device from a different vendor.
The encapsulation frame-relay “ietf” command enables Frame Relay encapsulation and allows connection to a device from a different vendor.
25. Match the characteristics with the type of WAN link. (Not all options are use.)
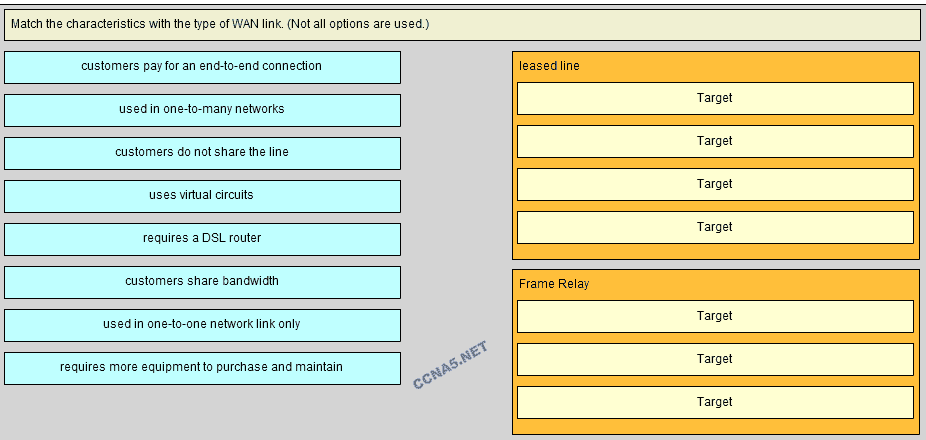
Place the options in the following order:
Leased line
[+] customers pay for an end-to-end connection
[+] customers do not share the line
[+] requires more equipment to purchase and maintain
[+] used in one-to-one network link only
[+] customers do not share the line
[+] requires more equipment to purchase and maintain
[+] used in one-to-one network link only
Frame Relay
[#] used in one-to-many networks
[#] uses virtual circuits
[#] customers share bandwidth
[#] uses virtual circuits
[#] customers share bandwidth
26. A network administrator uses the following command to configure a Frame Relay connection on a router towards the service provider:
R1(config-if)# frame-relay map ip 209.165.200.225 102 broadcast
What is the purpose of using the broadcast keyword?
R1(config-if)# frame-relay map ip 209.165.200.225 102 broadcast
What is the purpose of using the broadcast keyword?
to support IP address to MAC address resolution for the interface in the service provider site
to support dynamic routing protocol updates across the link*
to enable VoIP packet transmission across the link
to enable dynamic IP address-to-DLCI mapping
to support dynamic routing protocol updates across the link*
to enable VoIP packet transmission across the link
to enable dynamic IP address-to-DLCI mapping
27. What is an advantage of Frame Relay WAN technology compared with leased lines?
It uses one interface to connect to several remote sites.*
It offers a guaranteed direct electrical circuit from end to end.
It provides permanent dedicated capacity to the customers.
It supports both voice and data traffic.
It offers a guaranteed direct electrical circuit from end to end.
It provides permanent dedicated capacity to the customers.
It supports both voice and data traffic.
28. A network administrator of a large organization is designing a Frame Relay network. The organization needs redundancy between some key sites but not all. What WAN topology should the administrator choose to meet their needs?
partial mesh*
star
full mesh
extended star
star
full mesh
extended star
29. Match the descriptions to the Frame Relay transmission rate term. (Not all options are use.)
Place the options in the following order:
port speed –> the capacity of the local loop
– not scored –
excess burst size (Be) –> the bandwidth available above the CIR up to the access rate of the link
committed burst size (Bc) –> a negotiated rate above the CIR that the customer can use to transmit for short burst
committed information rate (CIR) –> the data transmission bandwidth guaranteed over the local loop by the service provider
port speed –> the capacity of the local loop
– not scored –
excess burst size (Be) –> the bandwidth available above the CIR up to the access rate of the link
committed burst size (Bc) –> a negotiated rate above the CIR that the customer can use to transmit for short burst
committed information rate (CIR) –> the data transmission bandwidth guaranteed over the local loop by the service provider
Post a Comment