CCNA 3 Scaling Networks Chapter 6 v5 Exam Answers 2016
1
The network administrator has been asked to summarize the routes for a new OSPF area. The networks to be summarized are 172.16.8.0, 172.16.10.0, and 172.16.12.0 with subnet masks of 255.255.255.0 for each network. Which command should the administrator use to forward the summary route for area 15 into area 0?
The network administrator has been asked to summarize the routes for a new OSPF area. The networks to be summarized are 172.16.8.0, 172.16.10.0, and 172.16.12.0 with subnet masks of 255.255.255.0 for each network. Which command should the administrator use to forward the summary route for area 15 into area 0?
area 15 range 172.16.8.0 255.255.255.248
area 0 range 172.16.8.0 255.255.248.0
area 0 range 172.16.8.0 255.255.255.248
area 15 range 172.16.8.0 255.255.248.0*
2
Fill in the blank.
The ” backbone ” area interconnects with all other OSPF area types.
Fill in the blank.
The ” backbone ” area interconnects with all other OSPF area types.
3. Match each type of OSPF router to its description. (Not all options are used.)

Place the options in the following order:
backbone router -> a router in the backbone area
– not scored –
internal router -> a router with all its interfaces in the same area
Autonomous System Boundary Router -> a router that has at least one interface that is attached to a non-OSPF network
Area Border Router -> a router with its interfaces attached to multiple areas
backbone router -> a router in the backbone area
– not scored –
internal router -> a router with all its interfaces in the same area
Autonomous System Boundary Router -> a router that has at least one interface that is attached to a non-OSPF network
Area Border Router -> a router with its interfaces attached to multiple areas
4
Fill in the blank. Do not use acronyms.
OSPF type 2 LSA messages are only generated by the ” DR ” router to advertise routes in multiaccess networks.
Fill in the blank. Do not use acronyms.
OSPF type 2 LSA messages are only generated by the ” DR ” router to advertise routes in multiaccess networks.
5
What is one advantage of using multiarea OSPF?
What is one advantage of using multiarea OSPF?
It improves the routing efficiency by reducing the routing table and link-state update overhead.*
It enables multiple routing protocols to be running in a large network.
It increases the routing performance by dividing the neighbor table into separate smaller ones.
It allows OSPFv2 and OSPFv3 to be running together.
6
A network administrator is verifying a multi-area OSPF configuration by checking the routing table on a router in area 1. The administrator notices a route to a network that is connected to a router in area 2. Which code appears in front of this route in the routing table within area 1?
A network administrator is verifying a multi-area OSPF configuration by checking the routing table on a router in area 1. The administrator notices a route to a network that is connected to a router in area 2. Which code appears in front of this route in the routing table within area 1?
O IA*
O
C
O E2
7
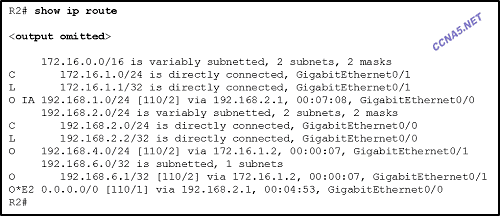
Refer to the exhibit. What can be concluded about network 192.168.4.0 in the R2 routing table?
This network should be used to forward traffic toward external networks.
The network was learned from a router within the same area as R2.*
The network was learned through summary LSAs from an ABR.
The network can be reached through the GigabitEthernet0/0 interface.
8
An ABR in a multiarea OSPF network receives LSAs from its neighbor that identify the neighbor as an ASBR with learned external networks from the Internet. Which LSA type would the ABR send to other areas to identify the ASBR, so that internal traffic that is destined for the Internet will be sent through the ASBR?
An ABR in a multiarea OSPF network receives LSAs from its neighbor that identify the neighbor as an ASBR with learned external networks from the Internet. Which LSA type would the ABR send to other areas to identify the ASBR, so that internal traffic that is destined for the Internet will be sent through the ASBR?
LSA type 1
LSA type 2
LSA type 3
LSA type 4*
LSA type 5
9
Which three steps in the design and implementation of a multiarea OSPF network are considered planning steps? (Choose three.)
Which three steps in the design and implementation of a multiarea OSPF network are considered planning steps? (Choose three.)
Configure OSPF.
Define the OSPF parameters.*
Troubleshoot the configurations.
Gather the required parameters.*
Define the network requirements.*
Verify OSPF.
10
Fill in the blank. Use a number.
An ASBR generates type ” 5 ” LSAs for each of its external routes and floods them into the area that it is connected to.
Fill in the blank. Use a number.
An ASBR generates type ” 5 ” LSAs for each of its external routes and floods them into the area that it is connected to.
11

Refer to the exhibit. What is indicated by the O IA in the router output?
The route was learned from within the area.
The route was learned from outside the internetwork.
The route was manually configured.
The route was learned from another area.*
12
Which command can be used to verify the contents of the LSDB in an OSPF area?
Which command can be used to verify the contents of the LSDB in an OSPF area?
show ip route ospf
show ip ospf database*
show ip ospf interface
show ip ospf neighbor
13
Which statement describes a multiarea OSPF network?
Which statement describes a multiarea OSPF network?
It has a core backbone area with other areas connected to the backbone area.*
It has multiple routers that run multiple routing protocols simultaneously, and each protocol consists of an area.
It consists of multiple network areas that are daisy-chained together.
It requires a three-layer hierarchical network design approach.
14
Which characteristic describes both ABRs and ASBRs that are implemented in a multiarea OSPF network?
Which characteristic describes both ABRs and ASBRs that are implemented in a multiarea OSPF network?
They usually have many local networks attached.
They both run multiple routing protocols simultaneously.
They are required to perform any summarization or redistribution tasks.*
They are required to reload frequently and quickly in order to update the LSDB.
15
Where can interarea route summarization be performed in an OSPF network?
Where can interarea route summarization be performed in an OSPF network?
ABR*
any router
DR
ASBR
16

Refer to the exhibit. Which two statements are correct? (Choose two.)
The entry for 172.16.200.1 represents a loopback interface.
To reach network 172.16.2.0, traffic will travel through the GigabitEthernet0/0 interface.
To reach network 192.168.1.0, traffic will exit via the Serial0/0/0 interface.*
The routing table contains routes from multiple areas.*
The routing table contains two intra-area routes.
17
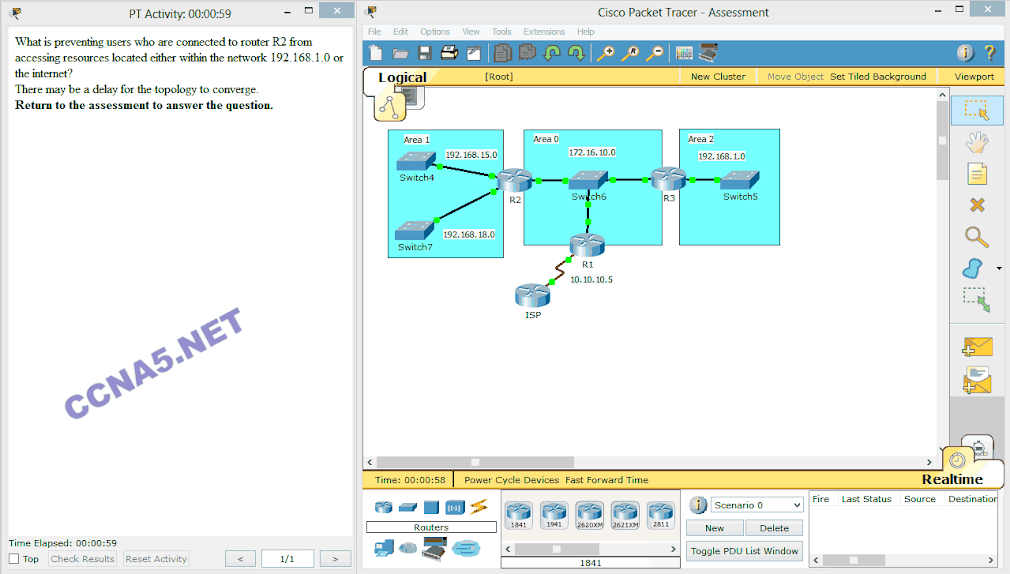
Launch PT Hide and Save PT
Open the PT Activity. Perform the tasks in the activity instructions and then answer the question.
What is preventing users who are connected to router R2 from accessing resources located either within the network 192.168.1.0 or the internet?
Open the PT Activity. Perform the tasks in the activity instructions and then answer the question.
What is preventing users who are connected to router R2 from accessing resources located either within the network 192.168.1.0 or the internet?
The router R2 is not receiving any updates from either router R1 or R3.*
The default route is not redistributed correctly from the router R1 by OSPF.
The OSPF timers that are configured on routers R1, R2, and R3 are not compatible.
The interface that is connected to the ISP is down.
The OSPF network statements are misconfigured on one of the routers.
18
Which two statements correctly describe OSPF type 3 LSAs? (Choose two.)
Which two statements correctly describe OSPF type 3 LSAs? (Choose two.)
Type 3 LSAs are used to update routes between OSPF areas.*
Type 3 LSAs are known as router link entries.
Type 3 LSAs are used for routes to networks outside the OSPF autonomous system.
Type 3 LSAs are known as autonomous system external LSA entries.
Type 3 LSAs are generated without requiring a full SPF calculation.*
19
A network administrator is implementing OSPF in a portion of the network and must ensure that only specific routes are advertised via OSPF. Which network statement would configure the OSPF process for networks 192.168.4.0, 192.168.5.0, 192.168.6.0, and 192.168.7.0, now located in the backbone area, and inject them into the OSPF domain?
A network administrator is implementing OSPF in a portion of the network and must ensure that only specific routes are advertised via OSPF. Which network statement would configure the OSPF process for networks 192.168.4.0, 192.168.5.0, 192.168.6.0, and 192.168.7.0, now located in the backbone area, and inject them into the OSPF domain?
r1(config-router)# network 192.168.0.0 0.0.0.255 area 1
r1(config-router)# network 192.168.4.0 0.0.255.255 area 0
r1(config-router)# network 192.168.4.0 0.0.15.255 area 1
r1(config-router)# network 192.168.0.0 0.0.3.255 area 0
r1(config-router)# network 192.168.4.0 0.0.3.255 area 0*
r1(config-router)# network 192.168.4.0 0.0.3.255 area 1
20
Which two networks are part of the summary route 192.168.32.0/22? (Choose two.)
Which two networks are part of the summary route 192.168.32.0/22? (Choose two.)
192.168.35.0/24*
192.168.36.0/24
192.168.33.0/24*
192.168.31.0/24
192.168.37.0/24
192.168.38.0/24
21

Refer to the exhibit. Fill in the blank. Do not use abbreviations.
The “network 192.168.10.128 0.0.0.127 area 1” command must be issued to configure R1 for multiarea OSPF.
22. Open the PT Activity. Perform the tasks in the activity instructions and then answer the question.
Fill in the blank. Do not use abbreviations.
What is the missing command on router R2 to establish an adjacency between routers R1 and R3?
Fill in the blank. Do not use abbreviations.
What is the missing command on router R2 to establish an adjacency between routers R1 and R3?
-> network 172.16.10.0 0.0.0.255 area 0 <-
23. What routing table descriptor is used to identify OSPF summary networks that originate from an ABR?
O E1
O E2
O
O IA*
O E2
O
O IA*
24. What is used to facilitate hierarchical routing in OSPF?
autosummarization
the election of designated routers
frequent SPF calculations
the use of multiple areas*
the election of designated routers
frequent SPF calculations
the use of multiple areas*
25. What type of OSPF LSA is originated by ASBR routers to advertise external routes?
type 2
type 3
type 1
type 5*
type 3
type 1
type 5*
26. What OSPF LSA type is used to inform routers of the router ID of the DR in each multiaccess network in an OSPF area?
type 1
type 4
type 3
type 2*
type 4
type 3
type 2*
27. Why do OSPF serial interfaces usually require manual bandwidth configuration?
Bandwidth value affects the actual speed of the link.
Each side of an OSPF serial link should be configured with a unique value.
OSPF uses the bandwidth value to compute routes for its routing table.*
All serial interfaces default to a value of 1.544 Mb/s.
Each side of an OSPF serial link should be configured with a unique value.
OSPF uses the bandwidth value to compute routes for its routing table.*
All serial interfaces default to a value of 1.544 Mb/s.
28. Refer to the exhibit.
After attempting to enter the configuration that is shown in router RTA, an administrator receives an error and users on VLAN 20 report that they are unable to reach users on VLAN 30. What is causing the problem?
RTA is using the same subnet for VLAN 20 and VLAN 30.*
There is no address on Fa0/0 to use as a default gateway.
Dot1q does not support subinterfaces.
The no shutdown command should have been issued on Fa0/0.20 and Fa0/0.30.
There is no address on Fa0/0 to use as a default gateway.
Dot1q does not support subinterfaces.
The no shutdown command should have been issued on Fa0/0.20 and Fa0/0.30.
29. Refer to the exhibit.
A network administrator has been asked to summarize the networks shown in the exhibit as part of a multiarea OSPF implementation. All addresses are using a subnet mask of 255.255.255.0. What is the correct summarization for these eight networks?
10.0.8.0 255.255.248.0
10.0.4.0 255.255.248.0
10.0.4.0 255.255.0.0
10.0.0.0 255.255.240.0*
10.0.4.0 255.255.248.0
10.0.4.0 255.255.0.0
10.0.0.0 255.255.240.0*
Post a Comment